Technology is bad…and good
During my last year in medical school, I was sitting on a bus on a cold winter day when I realized that my finger tips felt numb. I took off my gloves and watched the color of my fingers go from white to blue to red. I knew from my studies that this was Raynaud’s phenomenon and was caused by the blood vessels in my fingers becoming narrowed (going into spasm) due to the cold. I also knew that this was a relatively common problem in women. Unfortunately, I also knew that it could be a sign of something more serious, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. Medical students are known to be hypochondriacs and I went to see my physician the next day convinced that I was gravely ill. He was an incredibly warm and caring person and explained to me that he didn’t think it made sense to test for all the things it could be and that we should just see what happened over time. He reassured me and I felt better. This was doctor-patient communication at its best.
I believe strongly that the relationship between a doctor and a patient can lead to healing by itself. And there is little question that doctors have less time to listen to us than they did many years ago – in fact some studies suggest that it is as little as 7 or 8 minutes on average. And with more diagnostic tests available – specialized x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, etc – doctors are more likely to perform tests than take the time to listen to us. If they are using an electronic health record, they may seem more interested in entering information than in hearing what we have to say.
Think before you eat
We may be eating in unhealthy ways without realizing it. Even healthy foods can lead to problems in certain people – for example dairy products in people who are allergic to them or wheat in people who have celiac disease. But even if food does not cause a bad reaction in us, there is research evidence that we are not in as much control of what we are eating as we think we are.
The first problem is that we often eat without thinking. Dr. Brian Wansink at Cornell University has done some fascinating experiments (which he writes about in his book, Mindless Eating) that look at why we eat more than we think. In one experiment he had people eat bowls of soup while he watched them using hidden cameras. For some people, more soup was piped into the bowl (without them knowing it) as they were eating – it was a bottomless bowl. These people ate more soup than those who had a regular bowl. Similarly, he has shown in experiments that people will eat less food if they use a smaller plate. In yet another experiment, he went to a movie theatre where a first-run movie was playing just after lunch on a Saturday. He prepared popcorn in advance and made sure it was really stale but still safe to eat. He offered each person who bought a ticket a free soft drink and a bucket of popcorn (some buckets were medium in size and some were large but all were too big to finish). People who got the large containers, ate more popcorn (even though it was stale). He surveyed people when they were leaving the theatre and most people who had the large buckets said that they would not be fooled into eating more popcorn by a larger bucket.
Does food cause inflammation?
I am fascinated by food – what makes us eat the food we eat and how it affects our health. I’m especially interested when there is evidence to support the ideas.
As the American diet has changed in the past few decades, we have been gaining weight. It is also true that we are seeing more diseases – especially those that have an inflammatory component. Inflammation is when the body responds to things that shouldn’t be there – like an infection or a chemical – and the body sends cells to the area to fight them off. This can lead to pain and swelling, among other things. Some diseases caused by inflammation have “itis” at the end – arthritis, colitis, bronchitis, etc.
Is it possible that the food we eat is causing some of these diseases that are due to inflammation?
What’s the alternative?
A recent blog post on The Health Care Blog entitled Choosing Alternative Medicine raises some really interesting issues. The author, James Salwitz, MD complains that patients are turning to complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) therapies when they could be cured by “conventional” therapy. I think the real problem is that people are being treated with therapies that have not been proven to work when there are other more effective treatments available. Patients need to be given enough information about the research evidence to make informed choices. After learning about the evidence, if they choose a therapy that has not been proven to work when there are more effective treatments available, I would consider that an informed decision.
Rather than saying some medicines are “alternative” and some are “traditional” we should look at all treatments for which there is evidence to treat a particular condition. If there is evidence that an herbal remedy or vitamin works even if it is not as good as the evidence for a drug, patients should be able to make the right choice for them based on the evidence. Doctors need to be open to thinking about CAM therapies as treatment options if there is evidence to support their use.
The whole patient
 During my internship, I had an 18 year old patient with diabetes who I followed in my outpatient clinic (let’s call him Sam). He was first diagnosed at age 3 and had many hospitalizations thereafter for his poorly controlled diabetes. On one of these admissions, he arrived in the emergency room unconscious and near death because he hadn’t been taking his insulin. I happened to be on-call and stayed up with him all night managing his care. This required drawing blood tests every hour, adjusting medications, giving nutrients and fluids, etc. In the morning I had to present the situation to the physician in charge of my team at morning rounds. I proudly discussed how I had taken care of all of Sam’s problems throughout the night and how well he now looked. The senior physician asked me and the other interns and residents on our the team what the diagnosis was in this patient. We all looked at him like he was crazy since we had been talking about Sam’s diabetic emergency for the past 15 minutes. Then he told us that he thought the diagnosis was “communication failure”. Then we were convinced that he was crazy.
During my internship, I had an 18 year old patient with diabetes who I followed in my outpatient clinic (let’s call him Sam). He was first diagnosed at age 3 and had many hospitalizations thereafter for his poorly controlled diabetes. On one of these admissions, he arrived in the emergency room unconscious and near death because he hadn’t been taking his insulin. I happened to be on-call and stayed up with him all night managing his care. This required drawing blood tests every hour, adjusting medications, giving nutrients and fluids, etc. In the morning I had to present the situation to the physician in charge of my team at morning rounds. I proudly discussed how I had taken care of all of Sam’s problems throughout the night and how well he now looked. The senior physician asked me and the other interns and residents on our the team what the diagnosis was in this patient. We all looked at him like he was crazy since we had been talking about Sam’s diabetic emergency for the past 15 minutes. Then he told us that he thought the diagnosis was “communication failure”. Then we were convinced that he was crazy.
New types of evidence
It can be difficult to figure out how to use the results of research studies (randomized controlled trials or RCTs) to make a healthcare decision. There are many other problems with RCTs that may be less obvious.
First, to perform an RCT can take years – you need to get approval from the hospital where you are performing the study because you are doing research on humans. Then you need to get funding for the study so you may need to apply for some grants. After the study is completed, the results need to be analyzed; and then a paper needs to be written and submitted for publication to a journal. It could take years from the time the results are known until the time they are published.
Many commonly used treatments may not work
 A Washington Post WonkBlog piece entitled “Surprise! We don’t know if half our medical treatments work” got a lot of attention in social media circles. The title is a bit misleading but the concepts are really important. First, let me say that I worked at the BMJ for 8 years and was involved with the Clinical Evidence publication that is discussed in the blog so I may be a little biased!
A Washington Post WonkBlog piece entitled “Surprise! We don’t know if half our medical treatments work” got a lot of attention in social media circles. The title is a bit misleading but the concepts are really important. First, let me say that I worked at the BMJ for 8 years and was involved with the Clinical Evidence publication that is discussed in the blog so I may be a little biased!
The way doctors determine if medical treatments work is to perform research studies called randomized controlled trials (RCTs). These are studies where half the patients get a treatment and half get a placebo (or inactive treatment like a sugar pill) but the patients and the researchers do not know who is getting what. After a period of time (could be years), the researchers look at the results and figure out which group did better.
Communication, Innovation and Organization
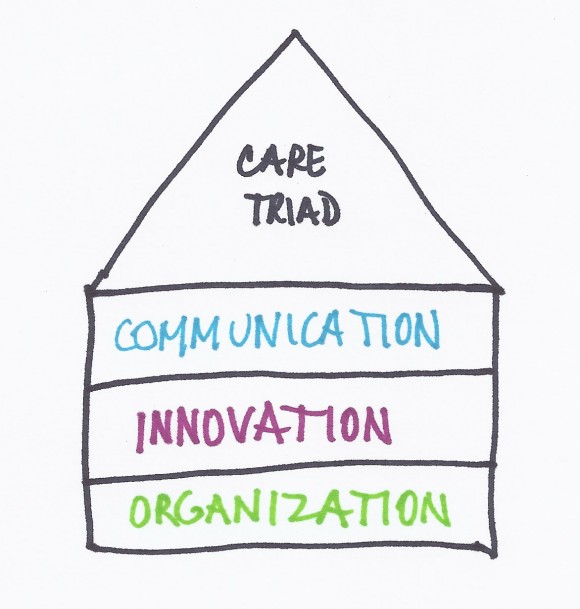 The Care Triad doesn’t really work without three important foundations – communication, innovation and organization.
The Care Triad doesn’t really work without three important foundations – communication, innovation and organization.
Communication requires that all members of the healthcare team understand that the patient is the most important person on the team. Patients should be spoken to in a respectful way starting with the person who sits at the welcome desk. Doctors need to learn to translate complicated medical information into ways that patients can understand it and patients need to learn to ask questions when they don’t understand what the doctor is saying. Doctors (and other members of the healthcare team), patients and family members also need to learn to talk openly about the end of life. Patients may also find it helpful to communicate with each other in online communities. Both doctors and patients need to learn to use social media to help themselves and each other, recognizing the power of personal experiences.
The Evidence
 Before I went to medical school, I studied biology in college and did laboratory research. One of the reasons I went into medicine was that I liked science but like most doctors, I didn’t understand the science as well as I thought I did. The scientific literature – the studies that have been done to figure out which treatments work and which ones don’t – is what we call the evidence.
Before I went to medical school, I studied biology in college and did laboratory research. One of the reasons I went into medicine was that I liked science but like most doctors, I didn’t understand the science as well as I thought I did. The scientific literature – the studies that have been done to figure out which treatments work and which ones don’t – is what we call the evidence.
In many ways, the evidence is the most challenging part of the Care Triad.
During my medical training, I remember reading individual scientific papers and doing exactly what they said. That approach may be OK when there is only one study that has been done to look at a particular treatment. But once there are many studies available, you need to look at all of them and figure out what the totality of the research is saying. You might look at one study that says a particular treatment works but there may be 9 other studies that say the same treatment is useless. Focusing on one study is called “cherry picking” and lots of doctors do it without realizing it.
The Doctor
 I did my internal medicine residency at a city hospital where I knew I would have lots of autonomy and see a broad array of diseases. My coworkers and I were on-call every third night and were usually up all night. We did everything for ourselves – transporting patients from the emergency room to their hospital beds or to the x-ray department, drawing blood, etc. We were even expected to look at all of the patient’s laboratory specimens – urine, sputum, spinal fluid, etc. – under a microscope. We never asked a patient what he or she wanted – it never occurred to us that there was a choice.
I did my internal medicine residency at a city hospital where I knew I would have lots of autonomy and see a broad array of diseases. My coworkers and I were on-call every third night and were usually up all night. We did everything for ourselves – transporting patients from the emergency room to their hospital beds or to the x-ray department, drawing blood, etc. We were even expected to look at all of the patient’s laboratory specimens – urine, sputum, spinal fluid, etc. – under a microscope. We never asked a patient what he or she wanted – it never occurred to us that there was a choice.
Things are different now. It is impossible to keep up-to-date with all of the medical advances and there are now a huge number of tests available to diagnose diseases. No one person can manage all of the complexities of care so doctors have become more specialized. Medicine needs to become more of a team sport – where specialists work together as a team to help the patient. And doctors need to accept the roles of new types of care providers as team members such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners who may be especially suited to provide routine care. We also now recognize that physical therapy, occupational therapy and nutrition are integral elements of care and that stress management, acupuncture, weight loss, health coaching and numerous other interventions can improve health in certain situations. In addition to being able to work as part of a team and help coordinate the team, doctors need to recognize that the most important member of the team is the patient.